Improve your treatment outcome by choosing the best antidepressant based on methylation status.
If you’ve been struggling with depression and feel like your antidepressant isn’t helping—or worse, that it’s making your symptoms more severe—you may be taking the wrong medication. Choosing the best antidepressant requires more than just trial and error; it involves understanding your body’s unique biochemistry. Working with a physician who understands methylation can make all the difference when it comes to selecting the proper antidepressant, changing antidepressants safely, and improving long-term mental health.
Understanding Methylation and Its Impact on Depression and Schizophrenia:
Methylation plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine—both essential for mood stability. As much as 40% of patients with depression or schizophrenia are either overmethylated or undermethylated. The majority of this group (60-70%) are undermethylators, meaning they have low serotonin and dopamine activity. On the other hand, overmethylators have too much serotonin and dopamine activity. Knowing your methylation status is critical when switching antidepressants for depression or choosing the best antidepressant for your needs.
Why MTHFR Genetic Testing Isn’t Enough:
Many turn to MTHFR genetic testing for guidance, but this approach often falls short. MTHFR results don’t provide the full picture. Instead, Dr. Epstein recommends testing for histamine levels or using a Plasma Methylation Pathway Panel. These methods offer a clearer understanding of how your body manages neurotransmitters, making it easier to select the proper antidepressant and create a treatment plan tailored to your biochemical profile.
Choosing the Best Antidepressant for Your Methylation Status:
For Undermethylators (Low Serotonin and Dopamine):
- Fluoxetine (Prozac): Increases serotonin without significantly affecting dopamine levels.
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin): Increases both dopamine and norepinephrine, which helps improve motivation and energy.
- Aripiprazole (Abilify): Stabilizes dopamine by acting as a partial agonist, helping to balance dopamine levels without a strong increase or decrease.
For Overmethylators (High Serotonin and Dopamine):
- Mirtazapine (Remeron): Decreases serotonin activity while increasing norepinephrine, helping to balance neurotransmitter levels.
- Venlafaxine (Effexor): Increases serotonin and norepinephrine, with a mild effect on dopamine, suitable for those needing moderate increases.
- Olanzapine (Zyprexa): Decreases dopamine activity, particularly useful for managing high dopamine levels in overmethylators.
Nuance: The Role of Copper in Depression and Anxiety:
Beyond methylation, copper levels can have a significant impact on mental health. High copper can lead to depression, often coupled with severe anxiety. Elevated copper levels influence how your body converts dopamine into norepinephrine, which can leave you with low dopamine and high norepinephrine—an imbalance that contributes to mood instability. Testing for copper can reveal hidden biochemical imbalances that, when optimized, can either enhance antidepressant effectiveness or, in some cases, serve as a natural treatment to alleviate symptoms without medications. Managing copper imbalances is particularly important in individuals with a history of anxiety-driven depression.
Changing Antidepressants Safely:
Switching antidepressants for depression is sometimes necessary when your current medication isn’t working. However, changing antidepressants safely under medical supervision is crucial to minimize withdrawal symptoms and stabilize your mood. Dr. Epstein works closely with your primary doctor or psychiatrist to ensure this process is as smooth and safe as possible.
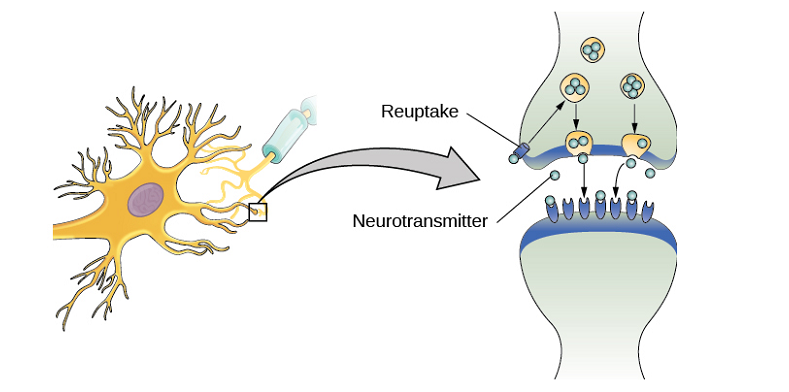
Discontinuing Antidepressant Medication with Nutrient-Based Support:
Dr. Epstein’s goal is to reduce the need for medications by supporting mental health with nutrient-based treatments. While discontinuing antidepressant medication is the ultimate aim, patients may need to stay on their medication initially to stabilize symptoms. Nutrients like SAMe, methionine, B12 or TMG can support neurotransmitter activity by reducing reuptake and thereby increasing activity, ultimately making it easier to eventually wean off medication.
Dr. Epstein and the Walsh Approach:
Dr. Epstein is a protégé of the Walsh Approach, a popular nutrient-based protocol for assessing and treating depression and other mood disorders with a customized nutrient protocol. This approach focuses on balancing your methylation status and biochemistry to support mental health naturally, making it easier to choose the best antidepressant or eventually reduce dependence on medication.
Next Steps:
If you feel your current antidepressant isn’t working or you’re experiencing unwanted side effects, it may be time for a consultation. Choosing the best antidepressant for your methylation status can significantly improve your mental health. Dr. Epstein will help you with selecting the proper antidepressant utilizing a thorough evaluation process, including histamine testing and a methylation panel plus a history taking. Whether you’re switching antidepressants or considering discontinuing them, Dr. Epstein provides personalized, nutrient-based support to ensure your mental health remains stable.
