Ozone Therapy: A Controversial Yet Promising Treatment
Despite its potential benefits, ozone therapy remains a controversial treatment in some circles, particularly in the United States, where the medical community is often more focused on pharmaceutical interventions. This controversy may be attributed to the lack of widespread acceptance of alternative remedies and supplements, rather than a lack of scientific evidence supporting ozone therapy's efficacy.
In recent years, a growing body of research has emerged, highlighting the potential therapeutic effects of ozone therapy. However, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional and carefully weigh the potential risks and benefits before undergoing ozone therapy. By working closely with a healthcare provider, you can determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific needs and health goals. This collaborative approach can help ensure that you receive the best possible care and support for your overall well-being.
Mitochondria and Energy Production
Mitochondria are tiny organelles present inside every cell of the human body except red blood cells. Mitochondria's main role is converting glucose from food and oxygen from breathing into energy, necessary for 90 percent of the energy cells require to function and thrive.
Mitochondria are the “the powerhouses of the cell” because they generate most of the cell’s supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy, and are involved in various other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth.
Ozone Therapy Worldwide and its Use in the United States
Ozone therapy is used more extensively in various countries worldwide, such as Russia, Cuba, Germany, Italy, and many others, compared to the United States. The difference in usage can be attributed to several factors, including regulatory policies, historical practices, and cultural perceptions of alternative therapies.
Some reasons why ozone therapy is not as common in the United States include regulatory constraints, a pharmaceutical-centric healthcare system, limited awareness and education, and skepticism and liability concerns.
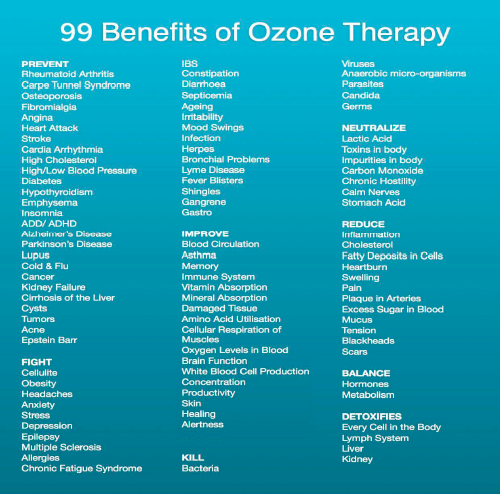
Despite these factors, ozone therapy has been purported to treat a wide range of conditions, including infections, wound healing, immune system support, detoxification, chronic fatigue and fibromyalgia, age-related diseases, and cancer.
Mechanisms of Action of Ozone Therapy
Here are some of the key mechanisms of action of ozone and oxygen on the cells in the body, which may explain their effectiveness in treating the purported conditions:
Oxidative stress modulation: Ozone therapy can induce a controlled and transient increase in oxidative stress, which in turn activates the body's antioxidant defense systems. This process can help neutralize and remove harmful free radicals, reduce inflammation, and promote cellular repair.
Improved oxygen delivery: Ozone can enhance the delivery of oxygen to tissues by improving blood circulation and oxygen release from red blood cells.
Antimicrobial effects: Ozone has potent antimicrobial properties due to its ability to disrupt the cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and parasites, as well as damage the genetic material of viruses.
Immune system modulation: Ozone therapy can stimulate the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response.
Enhanced energy production: Ozone can improve mitochondrial function, which is crucial for cellular energy production.
Apoptosis induction: Ozone has been shown to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in some cancer cells, which may explain its potential use as an adjunct treatment for cancer.
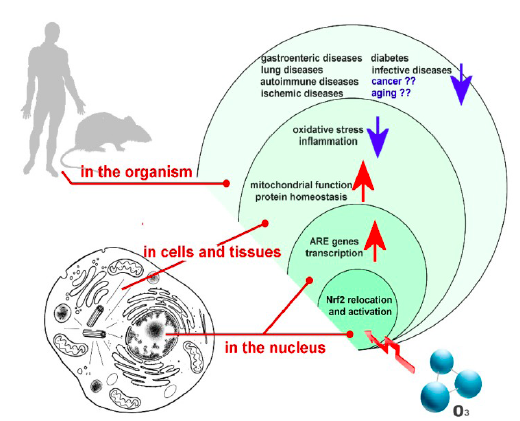
Ozone-stimulated glutathione production:
- Ozone exposure: When ozone is introduced into the body, it reacts with various biomolecules, such as lipids and proteins, generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid oxidation products (LOPs).
- Oxidative stress induction: The increase in ROS and LOPs causes a transient oxidative stress in the cells, which acts as a signal for the activation of various cellular defense mechanisms.
- Activation of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway: The oxidative stress triggers the activation of the Nrf2 pathway, a key regulator of cellular antioxidant response. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that, when activated, translocates to the cell nucleus and binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE) in the promoter region of various antioxidant genes, including those involved in glutathione synthesis.
- Upregulation of glutathione synthesis: The activation of the Nrf2 pathway leads to the upregulation of genes encoding for the enzymes involved in glutathione synthesis, such as glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthetase (GS). GCL catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis by forming a dipeptide of glutamate and cysteine, while GS catalyzes the subsequent step, which is the addition of glycine to form glutathione.
- Increased glutathione levels: The upregulation of glutathione synthesis results in higher intracellular levels of glutathione, which can neutralize ROS, reduce inflammation, and protect cells from oxidative damage.
In summary, the transient oxidative stress induced by ozone exposure activates the Nrf2 pathway, leading to the upregulation of genes involved in glutathione synthesis and an increase in intracellular glutathione levels. This mechanism is thought to contribute to the potential therapeutic effects of ozone therapy by enhancing the body's antioxidant defense systems and promoting cellular repair.

Methods of Ozone Therapy Application
Ozone therapy can be administered in various ways, depending on the condition being treated and the patient's preferences. Here are some common methods of ozone therapy application, along with their uses and benefits:
Rectal Insufflation
Rectal insufflation involves the introduction of ozone gas into the rectum, where it is absorbed by the intestinal mucosa. This method is less invasive than intravenous administration and can be done at home with proper equipment and guidance. It is commonly used for treating gastrointestinal conditions, boosting the immune system, and promoting overall wellness.
Intravenous Ten Pass (Major Autohemotherapy)
The ten-pass method, also known as major autohemotherapy, involves drawing blood from the patient, mixing it with ozone, and then reinfusing the ozonated blood back into the patient's bloodstream. This process is repeated ten times in a single session, hence the name "ten pass." This method is known for its ability to deliver a high concentration of ozone to the body, making it suitable for treating various conditions, including chronic infections, Lyme disease, and autoimmune disorders.
Prolozone Therapy
Prolozone therapy is a form of regenerative injection therapy, where a mixture of ozone, oxygen, and other therapeutic substances is injected directly into damaged or inflamed joints, tendons, and ligaments. This method aims to stimulate the body's healing response, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. Prolozone therapy is commonly used to treat chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, sports injuries, and degenerative joint diseases.
Ozone Bagging
Ozone bagging involves enclosing a body part, such as a limb, in a plastic bag filled with ozone gas. This method allows the ozone to penetrate the skin and underlying tissues, promoting healing and reducing inflammation. Ozone bagging is often used to treat localized infections, wounds, ulcers, and skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
Drinking Ozonated Water
Drinking ozonated water involves consuming water that has been infused with ozone gas. This method is thought to help improve gut health, support the immune system, and promote detoxification. However, the effectiveness of drinking ozonated water is still a matter of debate, and further research is needed to establish its true benefits.
Inhalation of Ozonides
Inhalation of ozonides refers to breathing in ozone gas that has been converted into more stable compounds called ozonides. This method is used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and sinusitis. It is crucial to note that direct inhalation of ozone gas can be harmful to the lungs and should be avoided. Ozonides are considered safer for inhalation, but caution is still necessary, and this therapy should be administered under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
The Role of Oxygen in Human Physiology and Biochemistry and Alternative Oxygen Therapies
Oxygen is an essential element for life, and humans have evolved with it, depending on it for a variety of vital physiological and biochemical processes. Understanding the importance of oxygen in the body and exploring other therapies that offer similar benefits to ozone therapy can provide additional options for maintaining optimal health.
Oxygen in the body:
Oxygen plays a crucial role in the human body's physiology and biochemistry. Some of its key functions include:
- Energy production: Oxygen is required for cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This process takes place within the mitochondria, where oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling the efficient production of ATP.
- Cellular function: Oxygen is involved in many cellular processes, including the synthesis of nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids.
- Immune function: Oxygen is needed for the proper functioning of the immune system, including the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are involved in antimicrobial defense and the regulation of inflammation.
- Detoxification: Oxygen is essential for the breakdown and elimination of toxins and waste products through processes such as oxidation and hydroxylation.
Alternative oxygen therapies for ozone related benefits:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity increases the body's demand for oxygen, which in turn enhances blood circulation, oxygen delivery to tissues, and overall cardiovascular health. Exercise can also stimulate the production of antioxidants and promote cellular repair and regeneration.
- Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT): EWOT involves exercising while breathing in higher concentrations of oxygen, typically through a mask connected to an oxygen concentrator. This therapy is thought to improve oxygen delivery to tissues, enhance energy production, and promote the release of growth factors and anti-inflammatory molecules.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): HBOT involves the inhalation of 100% oxygen at pressures greater than atmospheric pressure in a specialized chamber. The increased pressure allows for greater oxygen dissolution in the blood, which can help enhance tissue oxygenation, reduce inflammation, and promote healing in various conditions such as wounds, infections, and neurological disorders.
In conclusion, oxygen is an indispensable element for life, playing a critical role in a wide range of physiological and biochemical processes in the human body. Ozone therapy, exercise, EWOT, and HBOT are just a few of the many therapies that harness the power of oxygen to promote health and well-being. Each of these therapies offers unique benefits, and the choice of therapy will depend on individual needs, preferences, and specific health conditions.