Understanding Pyrrole Disorder (also known as Pyroluria and Kryptopyrrole Disorder)
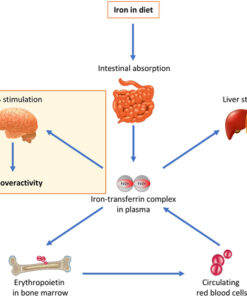
Pyrrole disorder is caused by an overproduction of a byproduct called hydroxyhemopyrrolin-2-one (HPL), which is formed during the synthesis of hemoglobin in the body. HPL is believed to bind with zinc and vitamin B6, which can lead to deficiencies in these nutrients, and can cause a range of symptoms.
The exact mechanisms by which HPL causes loss of zinc and vitamin B6 are not well understood, but it is thought that HPL binds with these nutrients and causes them to be excreted in the urine, resulting in reduced levels of these nutrients in the body. Zinc and vitamin B6 are both essential nutrients that play important roles in many biological processes in the body, including the immune system, brain function, and energy production.
Zinc is required for the activity of more than 300 enzymes in the body, including those involved in DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and immune function. Zinc deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including poor wound healing, hair loss, diarrhea, and an increased risk of infections.
Vitamin B6 is involved in many metabolic processes in the body, including the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. Deficiency in vitamin B6 can cause a range of symptoms, including depression, anxiety, irritability, and neurological symptoms such as numbness and tingling.
While pyrrole disorder is a controversial condition that is not recognized by mainstream medicine, some practitioners believe that it may be associated with deficiencies in zinc and vitamin B6, and recommend supplementation with these nutrients to address the symptoms of the condition. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between HPL, zinc, and vitamin B6, and to determine the best course of treatment for individuals with pyrrole disorder.
Symptoms Associated with Pyrrole Disorder:
The symptoms associated with pyrrole disorder can vary from person to person, but may include:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Insomnia
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Poor stress tolerance
- Joint pain and inflammation
- Digestive issues
- Behavioral problems in children
Zinc Deficiency Caused by Pyroluria
Zinc Role in the Nervous System:
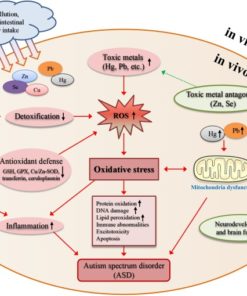
Zinc is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in many biological processes in the body, including the proper functioning of the nervous system. Zinc deficiency can result in a range of neurological problems, including:
- Cellular death: Zinc is an important regulator of cell death, and deficiency can disrupt the balance between cell survival and death, leading to increased cellular death in the brain and other tissues.
- Neurotransmitter production: Zinc is involved in the production and regulation of many neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and GABA. Deficiency can lead to a decrease in the production and activity of these neurotransmitters, which can result in mood disorders, anxiety, and other neurological problems.
- Oxidative stress: Zinc is a critical component of many antioxidant enzymes that balance the body's level of free radicals such as free copper thereby protecting cells from damage by free radicals. Deficiency can increase oxidative stress in the brain, which has been implicated in many neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- Biochemical reactions: Zinc is involved in many key biochemical reactions in the body, including DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and energy metabolism. Deficiency can disrupt these processes, leading to impaired brain function and neurological problems.
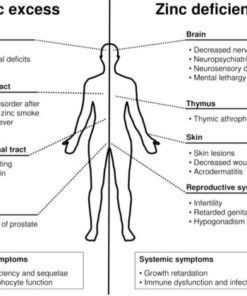
Signs and Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency:
Chronic zinc deficiency can lead to a range of signs and symptoms, including:
- Impaired growth and development: Zinc is important for normal growth and development, and chronic deficiency can lead to stunted growth in children and adolescents.
- Delayed wound healing: Zinc plays a critical role in the process of wound healing, and chronic deficiency can result in delayed wound healing and increased risk of infections.
- Skin problems: Chronic zinc deficiency can result in skin rashes, acne, and other skin problems.
- Diarrhea: Zinc is involved in maintaining the integrity of the gastrointestinal lining, and chronic deficiency can lead to chronic diarrhea.
- Impaired immune function: Zinc is essential for proper immune function, and chronic deficiency can lead to an increased risk of infections and a weakened immune system.
- Fatigue and weakness: Chronic zinc deficiency can result in feelings of fatigue, weakness, and decreased energy.
- Hair loss: Zinc is involved in the growth and maintenance of healthy hair, and chronic deficiency can result in hair loss.
- Loss of appetite: Chronic zinc deficiency can result in a loss of appetite and decreased sense of taste and smell.
- Cognitive and neurological problems: Chronic zinc deficiency has been linked to cognitive and neurological problems, including impaired learning and memory, depression, and anxiety.
Vitamin B6 Deficiency Caused by Pyroluria
Vitamin B6 Role in the Nervous System
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is another essential nutrient that plays a critical role in many biological processes in the body, including the proper functioning of the nervous system. Vitamin B6 deficiency can result in a range of neurological problems, including:
- Inflammation: Vitamin B6 is involved in the regulation of the immune system and can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Deficiency can lead to an increase in inflammation, which has been linked to many neurological disorders, including depression, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease.
- Conversion of homocysteine to glutathione: Vitamin B6 is required for the conversion of homocysteine to glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage. Deficiency can lead to an accumulation of homocysteine, which has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other neurological disorders.
- Neurotransmitter production: Vitamin B6 is involved in the production and regulation of many neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and GABA. Deficiency can lead to a decrease in the production and activity of these neurotransmitters, which can result in mood disorders, anxiety, and other neurological problems.
- Biochemical reactions: Vitamin B6 is involved in many key biochemical reactions in the body, including the synthesis of heme, a component of hemoglobin, and the metabolism of amino acids and carbohydrates. Deficiency can disrupt these processes, leading to impaired brain function and neurological problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency:
Chronic vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to a range of signs and symptoms, including:
- Anemia: Vitamin B6 is required for the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's tissues. Chronic deficiency can lead to anemia.
- Skin problems: Vitamin B6 is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and other proteins, and chronic deficiency can lead to skin rashes and other skin problems.
- Depression and anxiety: Vitamin B6 is involved in the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, and chronic deficiency can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
- Cognitive and neurological problems: Chronic vitamin B6 deficiency has been linked to cognitive and neurological problems, including impaired learning and memory, confusion, and irritability.
- Inflammation: Vitamin B6 plays a role in regulating inflammation in the body, and chronic deficiency can lead to chronic inflammation and increased risk of chronic diseases.
- Cardiovascular disease: Chronic vitamin B6 deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, as vitamin B6 is involved in the conversion of homocysteine to glutathione, an antioxidant that helps protect against cardiovascular disease.
- Weak immune system: Vitamin B6 is required for the proper functioning of the immune system, and chronic deficiency can lead to a weakened immune system and increased risk of infections.
- Fatigue and weakness: Chronic vitamin B6 deficiency can result in feelings of fatigue, weakness, and decreased energy.
Understanding Copper Overload
Testing for Copper Overload
Other Single Item Tests
All Cognoscopy Labs
All Cognoscopy Labs
All Cognoscopy Labs
Walsh Approach Test Panels