Cognoscopy Panel #2 – Hormone Screen
$449.00
Congnoscopy Test – Hormone Screen
SKU: Cog2
Categories: All Cognoscopy Labs, Cognoscopy Lab Panels for Alzheimer's & Dementia, Cognoscopy Panel 2, Other Lab Panels
Tags: Bredesen Alzheimer's Cognoscopy Labs, Cognoscopy
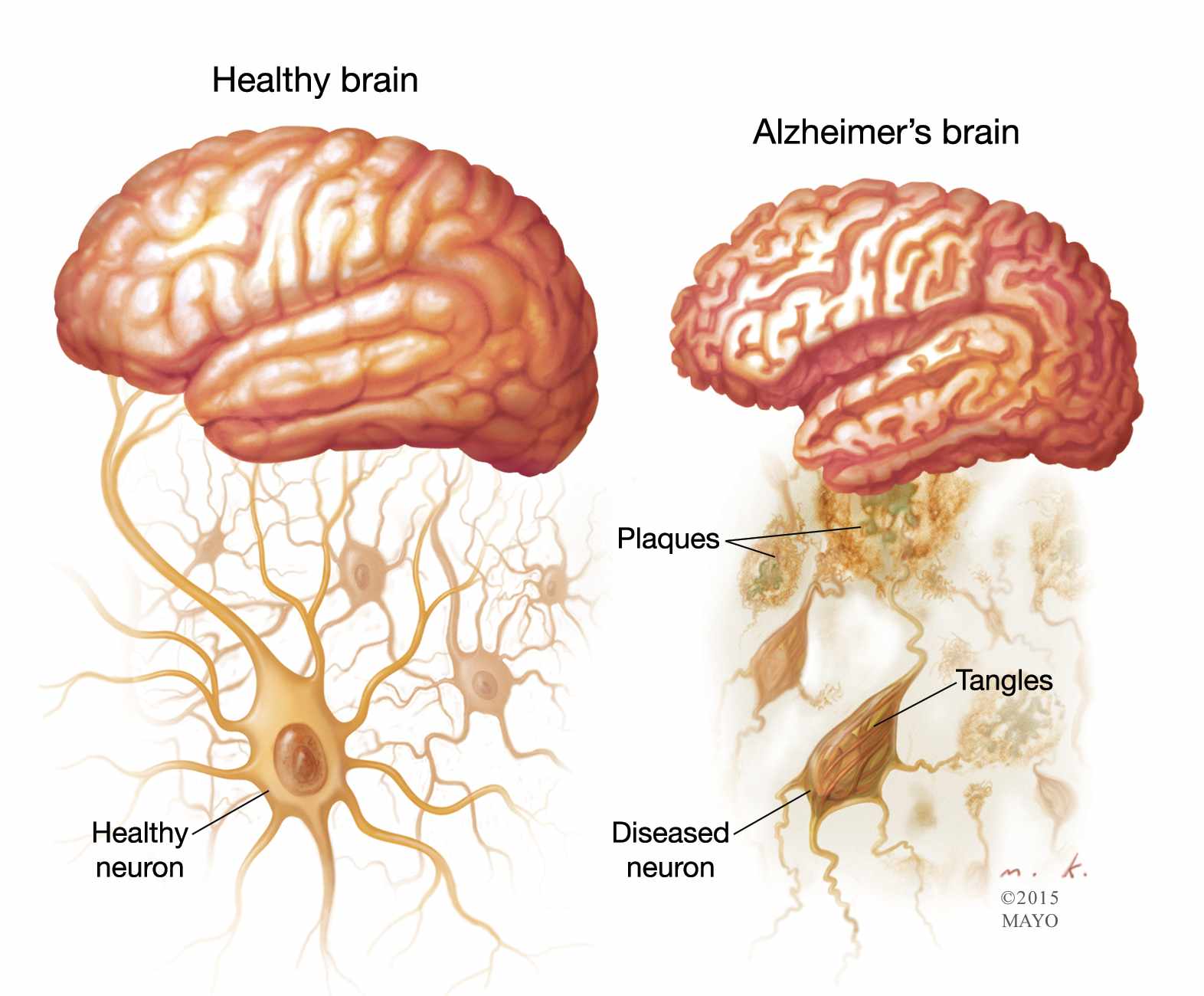
Cognoscopy Alzheimer's Hormone Panel
The hormones and elements offered here play various roles in the body and can have implications for brain health and the risk or progression of dementia.
| #83498 | 17-OH Progesterone LCMS |
| #82670 | Estradiol |
| #84140 | Pregnenolone, MS |
| #84144 | Progesterone |
| #84270 | Sex Horm Binding Glob, Serum |
| #84402, #84403 | Testosterone, Free/Tot Equilib |
| #84482 | Reverse T3, Serum |
| #84481 | T3, Free |
| #84439 | T4,Free(Direct) |
| #84443 | TSH |
| #82533 | Cortisol - AM |
| #82627 | DHEA-Sulfate |
- 17-OH Progesterone LCMS (#83498): This hormone is a precursor to other steroids, including cortisol. Abnormal levels can indicate disorders of the adrenal gland. While there's no direct established link between 17-OH progesterone and dementia, abnormal levels can disrupt the overall hormonal balance, which may indirectly impact cognitive health.
- Estradiol (#82670): Estradiol is a form of estrogen, a hormone known to have protective effects on the brain. Lower levels of estradiol, such as those occurring after menopause, have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia, including Alzheimer's disease. Estrogen is thought to have neuroprotective effects and plays a role in neurotransmitter activity and brain metabolism.
- Pregnenolone, MS (#84140): Pregnenolone is a precursor to many other steroid hormones. It has been studied for its potential cognitive-enhancing effects. Some research suggests that pregnenolone might play a role in memory function and could have protective effects against cognitive decline, but more research is needed.
- Progesterone (#84144): Like estrogen, progesterone is another hormone that can influence brain function. It has neuroprotective properties and is involved in the repair and growth of myelin, which insulates nerve fibers. Changes in progesterone levels can potentially impact brain health and cognitive function.
- Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) (#84270): SHBG regulates the availability of sex hormones in the body. Altered levels of SHBG can affect the levels of active hormones, including estrogen and testosterone, thus potentially impacting brain health and the risk of dementia.
- Testosterone, Free and Total (#84402, #84403): Testosterone levels have been linked to cognitive health in men. Low testosterone levels are associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. Testosterone is thought to have neuroprotective effects and plays a role in maintaining cognitive function.
- Reverse T3, Serum (#84482): Reverse T3 is an inactive form of the thyroid hormone. Elevated levels can indicate issues with thyroid function, which can affect brain health and cognitive function. Thyroid disorders are known to affect mood, memory, and cognitive function.
- T3, Free (#84481) and T4, Free (Direct) (#84439): These are active thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones are crucial for brain health and cognitive function. Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can affect cognitive abilities and have been associated with an increased risk of dementia.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) (#84443): TSH is a key regulator of thyroid function. Abnormal TSH levels, indicating either an underactive or overactive thyroid, can impact brain function. Thyroid disorders are linked to changes in memory, attention, and cognitive processing speed.
- Cortisol - AM (#82533): Cortisol is known as the stress hormone. Chronic high levels of cortisol can have detrimental effects on the brain, potentially leading to memory problems and increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
- DHEA-Sulfate (#82627): DHEA-S is a hormone involved in the production of other sex hormones. It is thought to have neuroprotective properties, and lower levels have been associated with aging and cognitive decline.
The balance and levels of these hormones can impact various aspects of brain health and function. They are involved in cognitive processes, mood regulation, and neuronal protection. Imbalances or abnormal levels can be indicative of underlying health issues that might contribute to cognitive decline and dementia. Monitoring and managing these hormonal levels is part of a comprehensive approach to maintaining cognitive health and reducing the risk of dementia.