Cognoscopy Panel #3 – Testing Glucose, Lipids and Inflammation
$239.00
Glucose, Lipids, Inflammation
Cognoscopy Panel #3 for Testing Glucose, Lipids and Inflammation
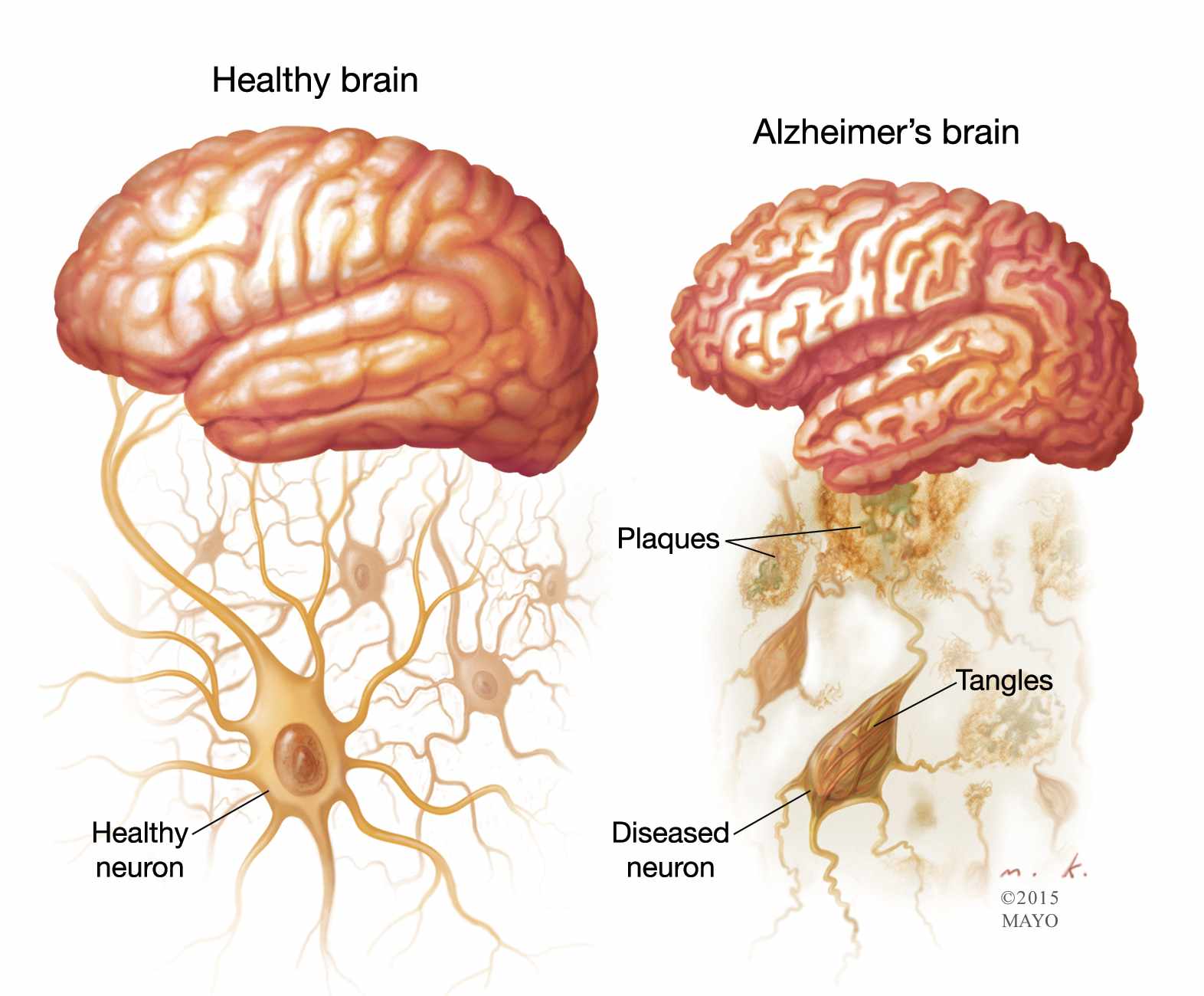
Understanding the relevance of various nutrient levels and biomarkers is crucial when assessing the risk and care needs for Alzheimer's disease. Each of these tests provides insight into different aspects of health that can be linked to the development or progression of Alzheimer's disease:
| Tests Included | Lab Code | CPT Code |
| Lipid Panel w/ Chol/HDL Ratio | 221010 | 80061 |
| C-Reactive Protein, Cardiac | 120766 | 86141 |
| Total Glutathione | 007700 | 82978 |
| Hemoglobin A1c | 001453 | 83036 |
| Insulin | 004333 | 83525 |
- Lipid Panel with Cholesterol/HDL Ratio (221010 80061): The lipid panel measures levels of various types of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. High levels of LDL ("bad") cholesterol and low levels of HDL ("good") cholesterol have been associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. This association is believed to be due to the role of cholesterol in amyloid plaque formation, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, dyslipidemia (abnormal lipid levels) can contribute to vascular health issues, which in turn can affect brain health.
- C-Reactive Protein, Cardiac (120766 86141): C-reactive protein (CRP) is a marker of inflammation in the body. Elevated levels of CRP are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, which is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease. Chronic inflammation is believed to play a role in the development of Alzheimer's disease, making CRP a useful marker for assessing risk.
- Total Glutathione (007700 82978): Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a key factor in the aging process and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Measuring glutathione levels can provide insight into the body's antioxidant capacity and potential vulnerability to oxidative stress-related damage in the brain.
- Hemoglobin A1c (001453 83036): Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a measure of average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. High HbA1c levels indicate poor blood sugar control, which is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, in turn, has been identified as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease. This connection is likely due to the effects of high blood sugar on blood vessels and inflammation, both of which can impact brain health.
- Insulin: Insulin regulates blood sugar levels and plays a role in brain function. Insulin resistance, a condition where the body's response to insulin is diminished, has been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. This condition leads to higher blood sugar and insulin levels, both of which can have detrimental effects on brain health. Understanding insulin levels can provide insight into metabolic health and its potential impact on cognitive function.
In summary, these tests offer valuable information about a person's metabolic, cardiovascular, inflammatory, and antioxidant status. All of these factors are important in understanding the risk and management of Alzheimer's disease, as they can influence brain health, cognitive function, and the potential progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Regular monitoring and management of these factors through lifestyle changes and medical interventions can be crucial in reducing the risk of Alzheimer's disease or slowing its progression.