Glucose Panel – Insulin, Free Insulin, HgA1c
$60.00
Insulin – Free & Total: #501561
Hemoglobin A1c: #001453
1. Insulin test: Insulin – Free & Total: #501561
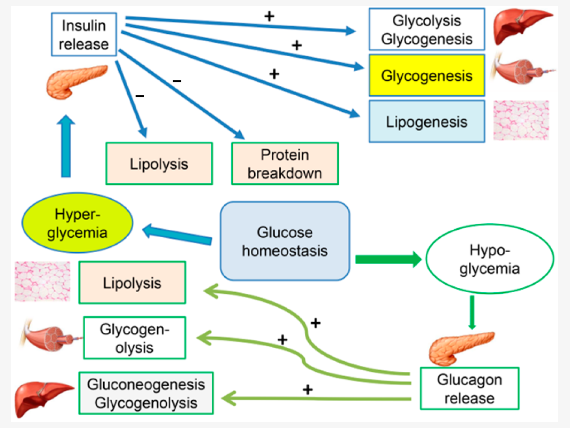
Use: An insulin test is primarily used to help diagnose conditions related to insulin, such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance. It can also be used to diagnose insulinomas (rare tumors that produce excess insulin) and other medical conditions that can cause hypoglycemia.
Indications: This test is typically indicated for patients who have symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), or who have risk factors for diabetes (such as obesity, family history of diabetes, history of gestational diabetes).
Potential Findings: High levels of insulin may suggest insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, or an insulin-producing tumor. Low levels could indicate type 1 diabetes. These results should always be interpreted in the context of other test results and clinical symptoms.
2. Free Insulin test:
Use: The Free Insulin test is used to measure the amount of insulin that is not bound to other proteins. It’s important for evaluating insulin resistance and understanding how much active insulin is in the body.
Indications: The test is indicated for individuals who have symptoms or risk factors for diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, or when healthcare providers want to assess the amount of unbound or bioactive insulin in the body.
Potential Findings: High levels of free insulin may indicate insulin resistance, and low levels may indicate a decreased capacity to produce insulin, like in type 1 diabetes.
3. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test: #001453
Use: HbA1c is used to measure the average blood glucose level over the past 2-3 months. It’s a cornerstone in the diagnosis, monitoring, and management of diabetes.
Indications: The test is typically indicated for diagnosing diabetes, prediabetes, and for monitoring how well a person’s diabetes is being managed over time.
Potential Findings: An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes. A level of 5.7 – 6.4% is considered prediabetes. If the HbA1c level is less than 5.7%, it’s normal. For those who already have diabetes, the goal is to have an HbA1c level below 7%, but this can vary depending on the individual’s overall health, age, and other factors.
Necessity: Regular testing of these markers is important for individuals at risk for or with diagnosed diabetes to help monitor and manage the condition. Early detection and management of abnormal insulin or blood glucose levels can prevent or delay the onset of complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage. It’s essential to note that these tests should be interpreted in the context of other laboratory findings and clinical symptoms, and treatment should be individualized to each patient’s needs.