Hepatitis Panel
$79.50
CPT 80074
SKU: 322744
Categories: Infections, Other Lab Panels, Other Single Item Tests
Tags: Infection, Liver
Hepatitis A antibody, IgM; hepatitis B core antibody, IgM; hepatitis B surface antigen; hepatitis C virus antibody
An acute viral hepatitis panel is used to help detect and/or diagnose acute liver infection and inflammation that is due to one of the three most common hepatitis viruses: hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), or hepatitis C virus (HCV).
This panel contains the following tests:
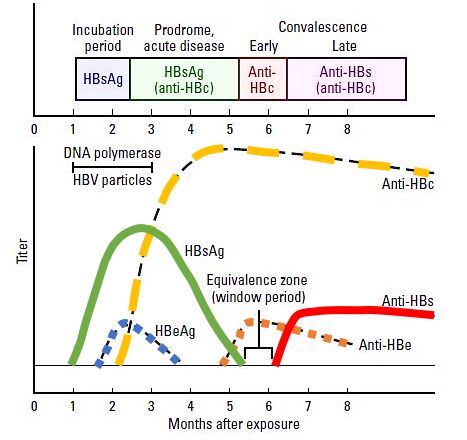
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) – A protein on the surface of the hepatitis B virus which can be detected in high levels during acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb) IgM – Positivity indicates recent infection with hepatitis B (≤6 months). Its presence along with the presence of HBsAg indicates acute infection.
- Hepatitis A antibody (HAAb) IgM – Acute Hepatitis A is diagnosed using this antibody which typically appears within four weeks of exposure and disappears within 3 months.
- Hepatitis C antibody (HCAb) – Antibodies to Hepatitis C appear in the blood two to four months after infection. Once infected with the hepatitis C virus, nearly 8 in 10 untreated people remain infected for life, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). It is recommended that positive results be confirmed through use of HCV RNA (qualitative) testing using a methodology called NAA and should be discussed with your doctor.