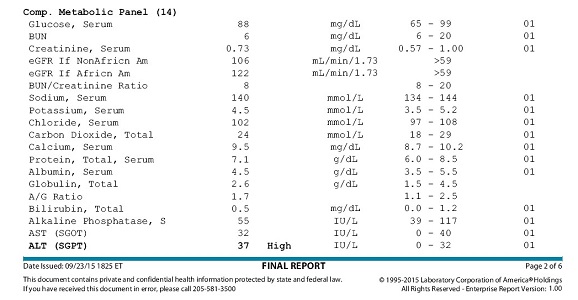
Comp. Metabolic Panel (14)
$29.00
CPT #80053
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel – 14 Analytes
This is a common metabolic panel used more for general assessment of kidneys and liver, electrolyte. It is not required for a Walsh Biotype assessment but can be useful in detecting other underlying issues.
The comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) is a frequently ordered panel of 14 tests that gives a healthcare provider important information about the current status of a person’s metabolism, including the health of the kidneys and liver, electrolyte and acid/base balance as well as levels of blood glucose and blood proteins. Abnormal results, and especially combinations of abnormal results, can indicate a problem that needs to be addressed.
The CMP includes the following tests:
- Glucose – energy source for the body; a steady supply must be available for use, and a relatively constant level of glucose must be maintained in the blood.
- Calcium – one of the most important minerals in the body; it is essential for the proper functioning of muscles, nerves, and the heart and is required in blood clotting and in the formation of bones.
Proteins
- Albumin – a small protein produced in the liver; the major protein in serum
- Total Protein – measures albumin as well as all other proteins in serum
Electrolytes
- Sodium – vital to normal body processes, including nerve and muscle function
- Potassium – vital to cell metabolism and muscle function
- CO2 (carbon dioxide, bicarbonate) – helps to maintain the body’s acid-base balance (pH)
- Chloride – helps to regulate the amount of fluid in the body and maintain the acid-base balance
Kidney Tests
- BUN (blood urea nitrogen) – waste product filtered out of the blood by the kidneys; conditions that affect the kidney have the potential to affect the amount of urea in the blood.
- Creatinine – waste product produced in the muscles; it is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys so blood levels are a good indication of how well the kidneys are working.
Liver Tests
- ALP (alkaline phosphatase) – enzyme found in the liver and other tissues, bone; elevated levels of ALP in the blood are most commonly caused by liver disease or bone disorders.
- ALT (alanine amino transferase, also called SGPT) – enzyme found mostly in the cells of the liver and kidney; a useful test for detecting liver damage
- AST (aspartate amino transferase, also called SGOT) – enzyme found especially in cells in the heart and liver; also a useful test for detecting liver damage
- Bilirubin – waste product produced by the liver as it breaks down and recycles aged red blood cells
Glucose
- Fasting blood sugar level – used to determine status of glucose for likelihood of hypoglycemia and diabetes.