TSH – Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
$38.00
CPT# 84443
Fasting Required: No
Specimen: Blood
Results: 1-3 Business Days
Description:
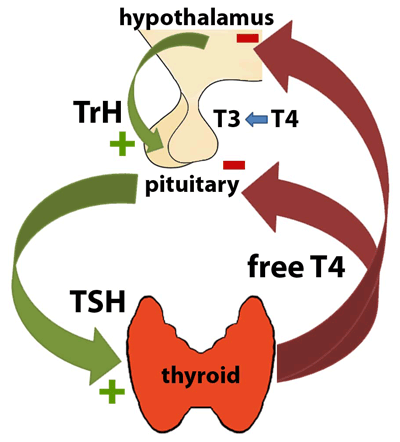
The best way to initially test thyroid function is to measure the TSH level in a blood sample. A high TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is failing because of a problem that is directly affecting the thyroid (primary hypothyroidism). The opposite situation, in which the TSH level is low, usually indicates that the person has an overactive thyroid that is producing too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism). Occasionally, a low TSH may result from an abnormality in the pituitary gland, which prevents it from making enough TSH to stimulate the thyroid (secondary hypothyroidism). In most healthy individuals, a normal TSH value means that the thyroid is functioning normally.
Methodology:
Immunoassay (IA)
Clinical Significance:
For differential diagnosis of primary, secondary, and tertiary hypothyroidism. Also useful in screening for hyperthyroidism. This assay allows adjustment of exogenous thyroxine dosage in hypothyroid patients and in patients on suppressive thyroxine therapy for thyroid neoplasia.
Alternative Name(s):
Thyrotropin, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Note: Result turn around times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.