Synonyms
- FK506
- Prograf®
- Protopic®
Test Details
Use
Tacrolimus is an immunosuppressive drug that is believed to prevent rejection in transplantation patients. Measurement of tacrolimus blood levels may be of use in monitoring patients receiving this drug.
Reference Interval
Clinical studies have shown that patients administered 0.07 mg/kg Prograf® obtain an optimal response to the drug at the following trough levels:
• Trough (immediately following transplant): 15.0 ng/mL
• Trough (steady-state, two weeks or more after transplant): 3.0−8.0 ng/mL
Additional Information
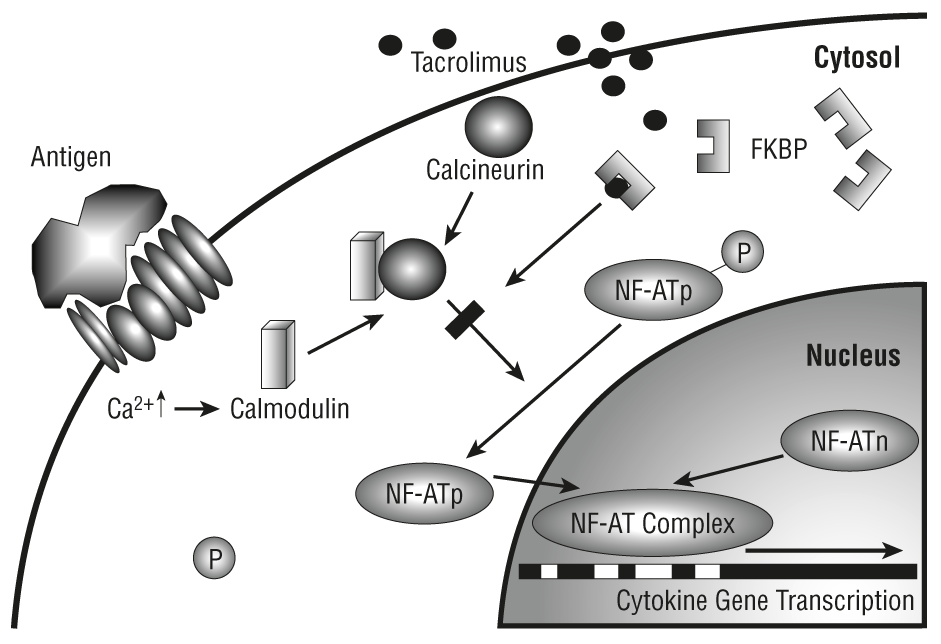
Tacrolimus, previously known as FK506, is an immunosuppressive drug derived from Streptomyces tsulenbaensis. It has been shown to be effective for the treatment of rejection following liver and kidney transplantations. Clinical trials are continuing for a variety of indications. Tacrolimus inhibits T-lymphocyte activation by inhibition of the phosphatase activity of calcineurin, although the exact mechanism of action is not known. Tacrolimus is bound to plasma proteins and is highly bound to erythrocytes (ratio of whole blood:plasma ranging from 12 to 67). Tacrolimus may be administered IV or orally. Absorption from the GI tract is variable and irregular. Peak blood concentrations are achieved at 1.5 to 3.5 hours. The elimination half-life from whole blood is 11.7 hours in liver transplant patients. Tacrolimus can cause nephrotoxicity, particularly when used in high doses. Care must be taken if tacrolimus is used in combination with other immunosuppressive drugs, particularly cyclosporine. Drugs found to increase tacrolimus levels include diltiazem, verapamil, clotrimazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole, voriconazole, clarithromycin, erythromycin, nelfinavir, ritonavir, as well as grapefruit juice. Decreased tacrolimus levels have been found with coadministration of rifampicin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, octreotide, and St John’s wort.1