Lipids, HbA1C
$45.00
CPT# 80061, 83036
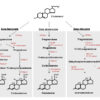
Lipid Panel
A lipid panel measures different types of fats (lipids) in the blood, providing information on cholesterol levels and overall heart health. The components typically include:
- Total Cholesterol: Measures the overall amount of cholesterol in the blood. High levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), including heart attacks and strokes.
- LDL Cholesterol (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” LDL carries cholesterol to the arteries, where it can build up and form plaques, leading to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). High LDL levels are a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- HDL Cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “good cholesterol,” HDL helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream, transporting it to the liver for excretion. Higher levels of HDL are protective against heart disease.
- Triglycerides: A type of fat in the blood that the body uses for energy. High levels of triglycerides can contribute to the risk of heart disease, especially when combined with low HDL or high LDL levels.
Conditions evaluated with a lipid panel:
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD): High LDL and triglyceride levels and low HDL are significant risk factors for heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Hyperlipidemia: High cholesterol or triglycerides, which can indicate poor lipid metabolism or lifestyle-related issues such as a high-fat diet, sedentary behavior, or obesity.
- Diabetes: Diabetics often have abnormal lipid levels, particularly elevated triglycerides and low HDL, due to insulin resistance.
- Metabolic Syndrome: A cluster of conditions including high triglycerides, low HDL, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
HbA1c measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months by assessing the percentage of hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells) that is glycated (attached to glucose). This test is commonly used to evaluate long-term glucose control.
- Normal HbA1c: Below 5.7%
- Pre-diabetes: HbA1c between 5.7% and 6.4%
- Diabetes: HbA1c of 6.5% or higher
Conditions evaluated with HbA1c:
- Diabetes: HbA1c is a critical test for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. It provides a long-term view of blood sugar control, which helps in managing treatment for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Pre-diabetes: Elevated HbA1c levels (but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes) indicate insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Poor blood sugar control, as indicated by high HbA1c levels, is a risk factor for heart disease and other cardiovascular complications.
What this panel helps evaluate:
- Diabetes and Pre-diabetes: HbA1c is essential for diagnosing and tracking blood sugar levels, while the lipid panel can show how diabetes affects lipid metabolism.
- Cardiovascular Risk: Both the lipid panel and HbA1c provide insights into the risk of heart disease. High cholesterol and poor glucose control are two major contributors to cardiovascular complications.
- Metabolic Syndrome: This panel is particularly useful in diagnosing metabolic syndrome, a condition characterized by a combination of high blood sugar, high triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, high blood pressure, and central obesity.
This panel is often ordered for patients at risk for, or being monitored for, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, or metabolic syndrome. It can help guide lifestyle interventions and medical treatments aimed at reducing these risks.